Geography
Location:
Bahrain is an island country located in the Persian Gulf, situated off the eastern coast of Saudi Arabia.

Topography:
The terrain of Bahrain is mostly flat and arid, with the highest point being the Jabal ad Dukhan hill. The country’s coastline is characterized by sandy beaches and shallow waters.
Climate:
Bahrain experiences a desert climate, with hot and humid summers and mild winters. The country is prone to dust storms, particularly during the summer months.
History
Ancient Civilization:
Bahrain has a rich history dating back to ancient times, with evidence of human settlement dating back over 5,000 years. The island has been inhabited by various civilizations, including the Dilmun civilization.
Modern Statehood:
Bahrain gained independence from British protection in 1971, becoming a sovereign state under the rule of the Al Khalifa family.
Political Reforms:
In recent years, Bahrain has undergone political reforms, including the establishment of a constitutional monarchy and the introduction of a bicameral parliament.

Leader
Current Leader:
Bahrain is a constitutional monarchy with the King, currently King Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa, serving as the head of state. The Prime Minister, appointed by the King, heads the government

Governance:
Bahrain’s governance structure includes a bicameral parliament, consisting of the Council of Representatives (elected by the public) and the Shura Council (appointed by the King). The country’s constitution guarantees rights such as freedom of speech and assembly.
Economic Overview
Main Sectors:
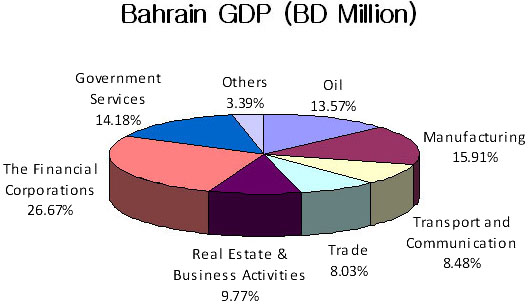
Bahrain’s economy is diversified, with significant contributions from sectors such as finance, tourism, manufacturing, and oil refining. The country is a regional financial hub and home to the Bahrain Financial Harbor.
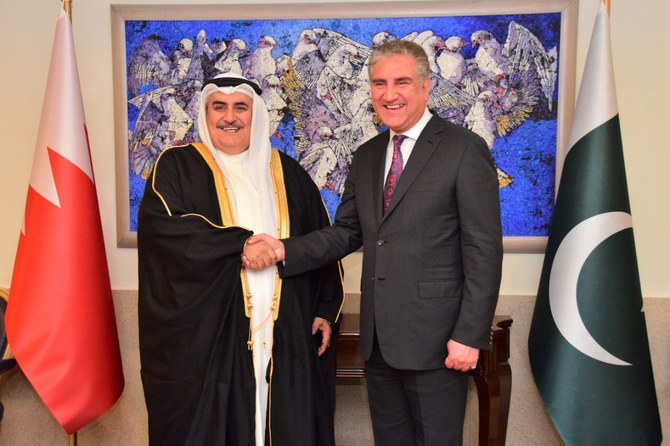
Relation with Pakistan:
Economic relations between Bahrain and Pakistan are modest but have potential for growth, particularly in trade, investment, and cooperation in sectors such as finance and tourism.

Strategic Importance
Financial Hub:
Bahrain plays a key role as a financial center in the Gulf region, attracting investment and serving as a gateway for business activities between the Middle East, Asia, and beyond.
Security Cooperation:
Bahrain maintains close security cooperation with regional allies, including Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, to address shared security challenges and maintain stability in the region.

Cultural and Social Aspects
Cultural Diversity: Bahrain is a multicultural society, with a diverse population consisting of Bahraini nationals, expatriate workers, and residents from various countries. The country’s cultural scene includes traditional Bahraini arts and heritage, as well as modern cultural events and festivals.
Expatriate Community:
Bahrain hosts a significant expatriate community, including workers from South Asia, particularly Pakistan, who contribute to the country’s economy and cultural exchange.





