Geography
Location:
Iran is in Western Asia, bordered by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan to the north, Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and Türkiye and Iraq to the west.

Topography:
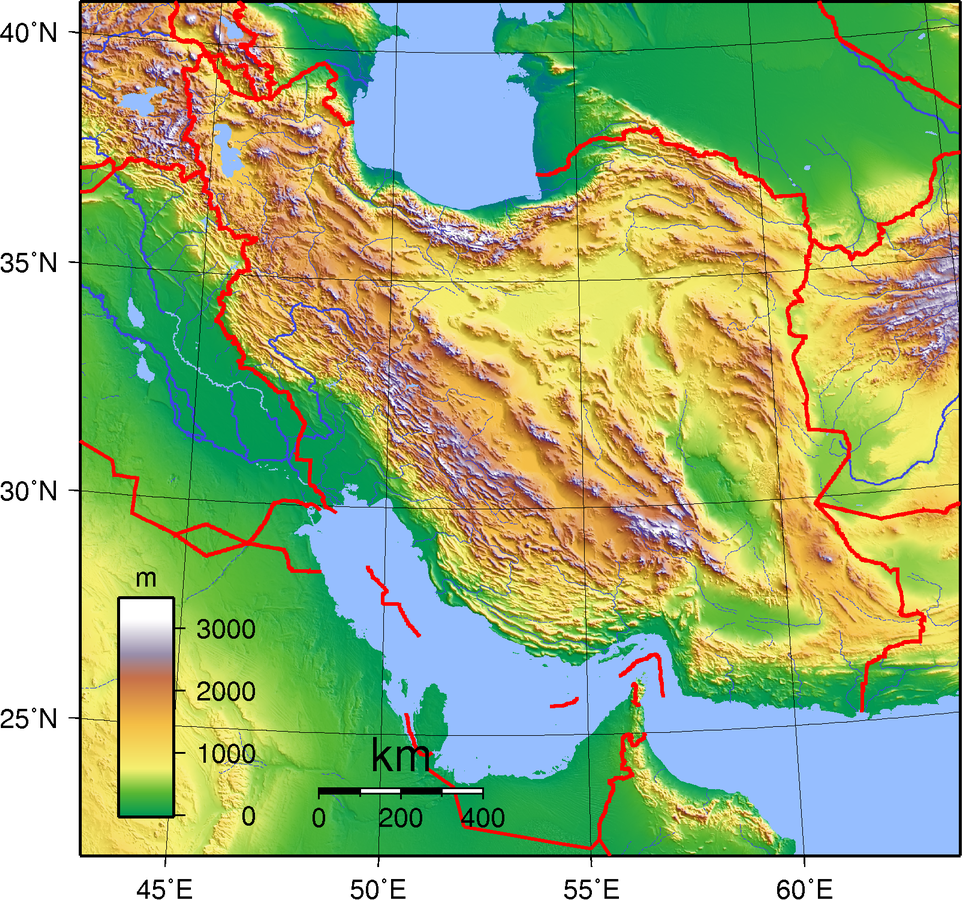
The country is characterized by diverse landscapes, including mountain ranges such as the Alborz and Zagros, vast deserts like the Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut, and coastal regions along the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
Climate:
Varied climate, ranging from arid and semi-arid to subtropical along the Caspian coast, with significant seasonal variations.
History
Ancient Civilization:
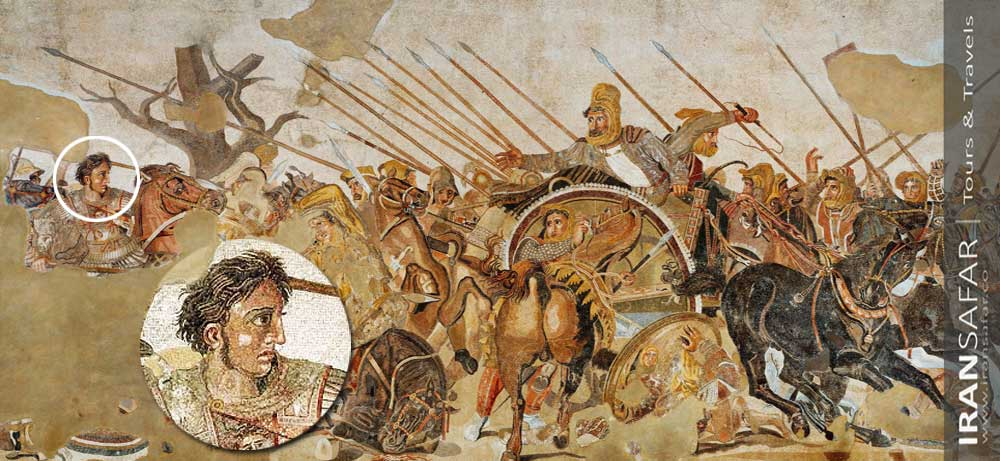
Iran boasts a rich historical heritage dating back to ancient civilizations such as the Elamites, Medes, and Achaemenids, known for their vast empire under Cyrus the Great.



Islamic Republic:
Following the 1979 Islamic Revolution, Iran became an Islamic Republic, with Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini as its first Supreme Leader.
Modern Developments:
Iran has faced international isolation due to its nuclear program and involvement in regional conflicts, while domestically experiencing political, social, and economic challenges.
Leader
Current Leader:
Iran operates under a unique political system led by a Supreme Leader, currently Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, who holds ultimate authority over state affairs. The President, currently Ebrahim Raisi, serves as the head of government.

Governance:
Iran is an Islamic Republic with a mixed system of democracy and theocratic governance, where religious figures and elected officials share power.
Economic Overview
Main Sectors:
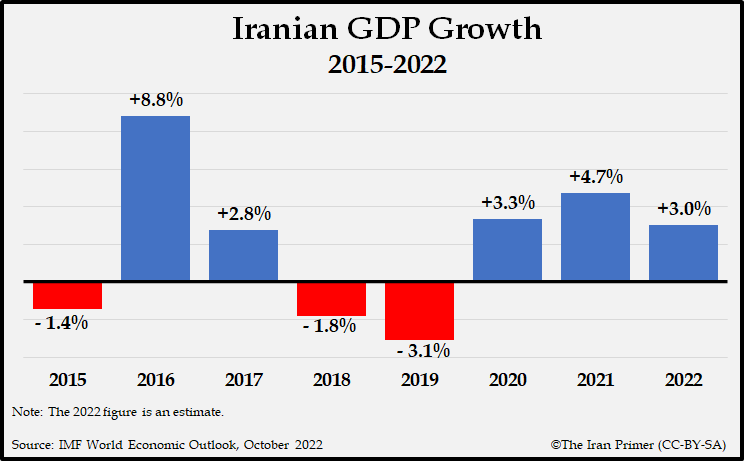
Iran’s economy is diversified, with significant contributions from oil and gas, agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Economic sanctions have hindered growth and development in recent years.
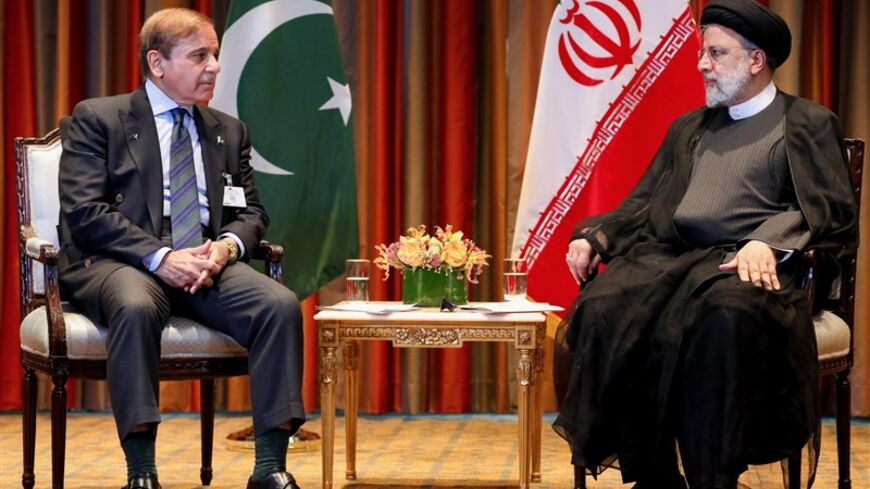
Relation with Pakistan:
Iran and Pakistan share economic ties in areas such as trade, energy, and infrastructure development. Projects like the Iran-Pakistan Gas Pipeline aim to enhance bilateral cooperation.

Strategic Importance
Regional Power:
Iran plays a significant role in regional geopolitics, with influence extending across the Middle East, particularly in Iraq, Syria, and Lebanon. Its relations with Pakistan are influenced by mutual security concerns, including border security and counter-terrorism efforts.

Nuclear Program: Iran’s nuclear program and its international implications have been a source of tension with the West, impacting global security and diplomatic relations.

Cultural and Social Aspects
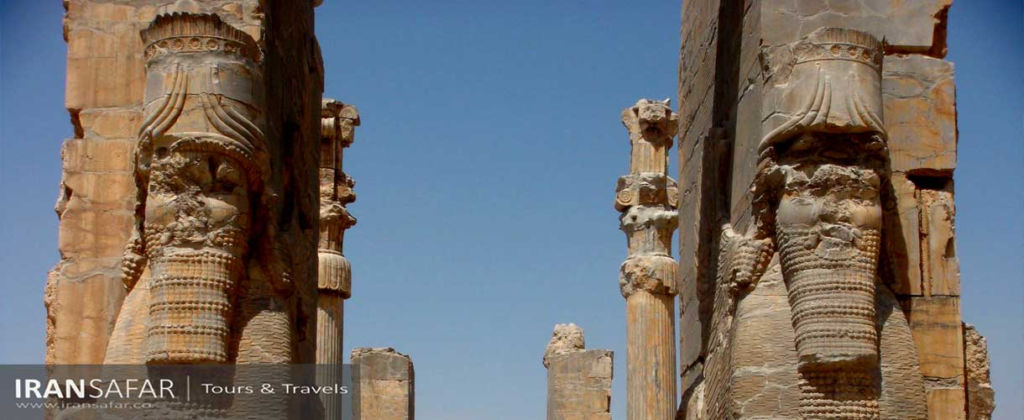
Cultural Heritage: Iran boasts a rich cultural heritage, including UNESCO World Heritage Sites like Persepolis and Isfahan’s Naqsh-e Jahan Square. Iranian culture, literature, and art have influenced the wider region for centuries.

Diaspora and Connections: The Iranian diaspora has a significant presence worldwide, with communities in countries like Pakistan contributing to cultural exchange and economic ties.


